How to File GSTR 2
GSTR-2 is based on auto populating GST return, which pops up only when the GSTR-1 is successfully submitted by the suppliers containing information about sales.
GSTR-2 is a GST Return to be filed by the 15th of every month [for the previous month] from the recipients of the goods / services and has auto filled columns containing the details, which the supplier has filled in GSTR-1. The recipients have either to approve or edit the transactions individually to avail the legitimate credit of the input tax.
Who should file GSTR-2?
All GST registered payers are liable to file GSTR-2 [irrespective of a zero transaction] except input service distributors, person opting compounding scheme, e-commerce operators, tax Deductor, tax collectors and non-resident dealers.
What does GSTR-2 contain?
Mostly, the headings under GSTR-2 are auto-populated from counter-party GST return and hence will involve minimal time to fill in, so think how to fill GSTR 2. There are 13 headings which form the framework of GSTR-2, detailed as under:
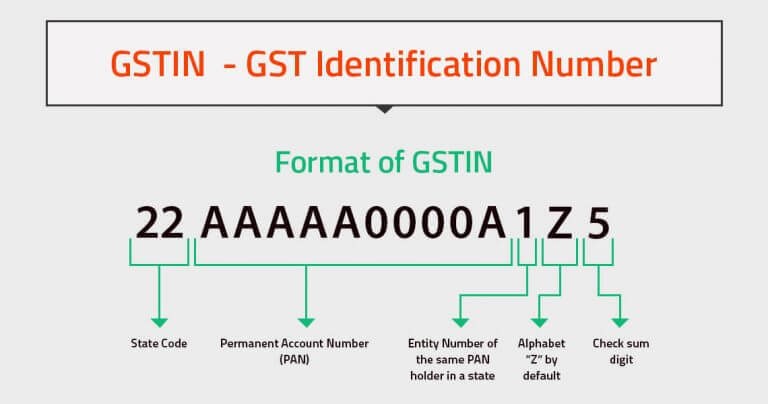
1. GSTIN: Goods and Services Taxpayer Identification Number
GSTIN, is a unique state-wise PAN based, alpha-numeric code assigned to each GST payer, which will auto-populate when the GSTR 2 form opens up and will look like this.
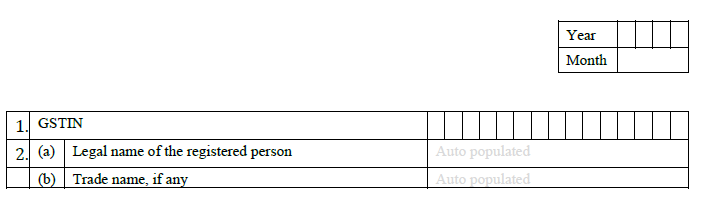
2. Name of the Taxpayer:
Both the individual and the trade name will also populate. Month and Year: The correct month and year for which the GSTR-2 is being filed, has to be filled in.
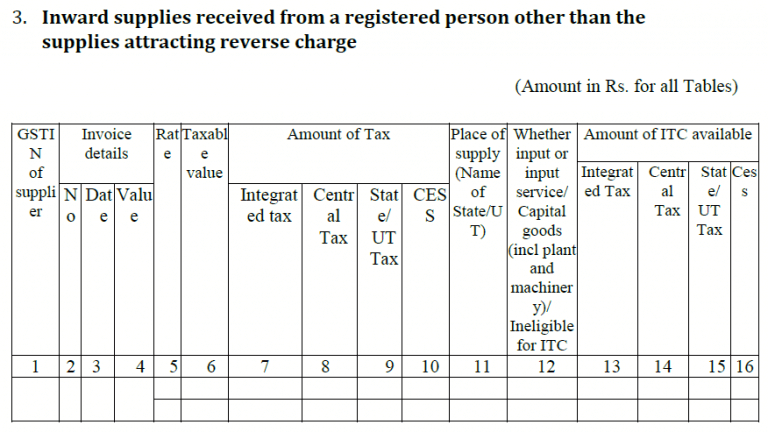
3. Inward Supplies received from a registered taxable person:
It will contain details of all purchases and the field based on auto-population of GSTR-2A having details about type, rate and amount of GST, eligibility of ITC and if it is applicable, then the amount of ITC.
Purchases made under reverse charge mechanism will not reflect here.
However, some specific transactions may not auto-populate because:
- Either, the seller did not file GSTR-1
- Or, the seller missed any transaction, while filing GSTR-1.
If either of this happens, the GSTR-2 allows to manually add these transactions and an auto-intimation will be sent to the seller to amend the same via GSTR-1A.
If the supply is received in more than one lot, the GSTR-2 must be filed in accordance with the date of the last lot of the supply received.
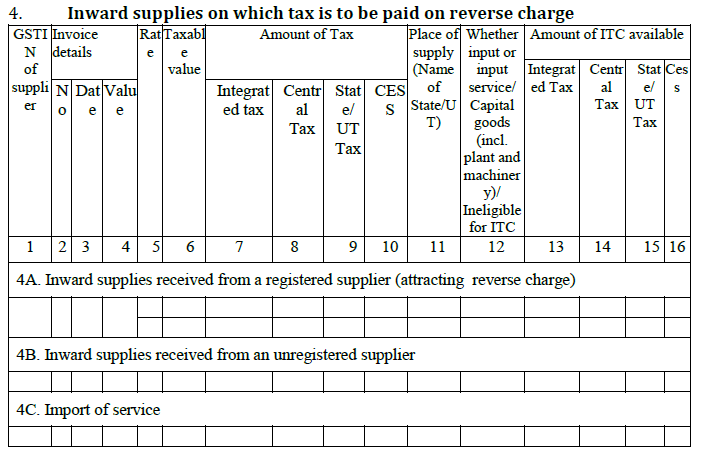
4. Inward supplies where tax is liable on reverse charge:
There are some goods and service which attract reverse charge, i.e. the GST is to be paid by the purchaser. Reverse charge is to be paid by a registered buyer, when he buys supplies of more than Rs. 5000/- per day from an unregistered seller.
This column will contain all the purchases on which reverse charge applies:
4A. This column contains all purchases [irrespective of amount] attracting reverse charge like buying agricultural produce from farmers.
4B. This column contains purchases of more than Rs. 5000/- from an unregistered seller.
4C. This column captures the reverse charge GST paid on import of service.
5. Inputs/Capital goods received from overseas or from SEZ units on a Bill of Entry:
All capital goods, goods received from SEZ or import of inputs [raw material for finished goods] received against a Bill of Entry are mentioned here.
5A. Imports:
All capital goods and import of inputs [raw material for finished goods] against a Bill of Entry are to be stated here. The 6 digit port code, 7 digit bill number (details of bill entry 13 digit) are to be filled.
5B. Supplies received from SEZ:
This section captures the inputs or capital goods received from sellers in a SEZ.
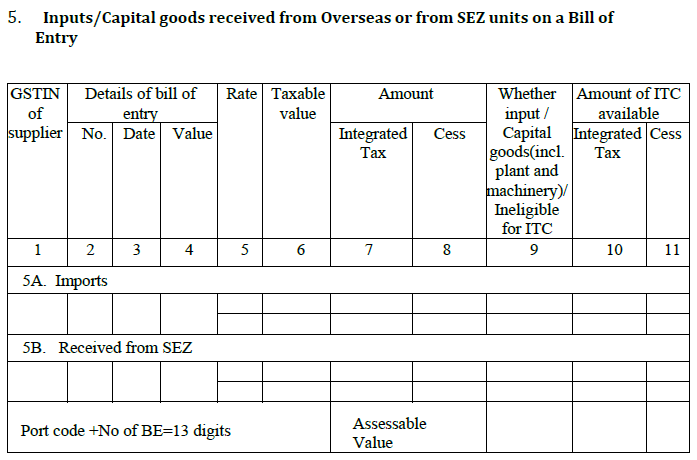
6. Amendments to details of inward supplies
The details of inward supplies given for earlier tax periods in tables 3, 4 and 5 [including issued debit notes/credit notes and their subsequent amendments] Once a GSTR is filed, it cannot be revised but only in the next month’s return under this section. The tax filer can manually amend the purchase details of the supplies with an auto-intimation to the seller. The seller then needs to change the details accordingly in his GSTR-1A return.
6A. All revisions of input goods/services [except Goods received from SEZ and imports] have to be mentioned here.
6B. The section will contain any changes in tax calculated on imported goods and also on goods from SEZ. The changes done in the bill of entry or import report must also be mentioned here.
6C. All the debit/credit notes [original] issued in accordance with the purchases are filled here. Any debit/credit note issued under reverse charge mechanism will get auto-populated here from counter-party GSTR-1 and other applicable returns.
6D. This heading captures any changes in the debit/credit notes of previous months.
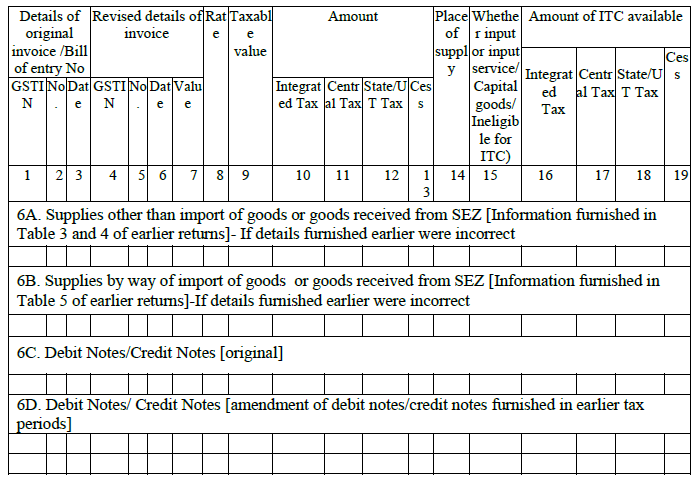
7. Supplies received from Composition Tax payers and from other exempt / nil rated non GST suppliers:
All the purchases from Composition Dealers and other exempt / nil rated non GST suppliers will be mentioned here. Non GST supplies like diesel and petrol and the supplies made in intra-state and inter-state will also be captured here.
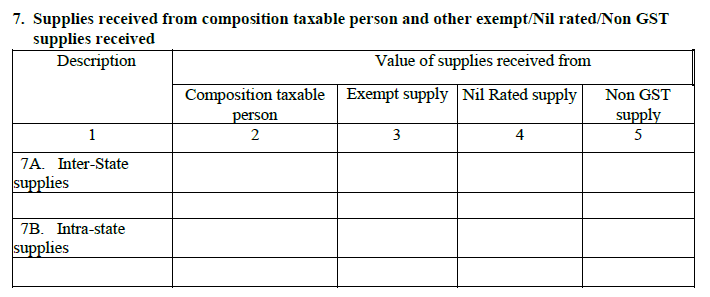
8. ISD credit received
This field auto-populates and has information about the ITC received from a registered Input Service Distributor [ISD]
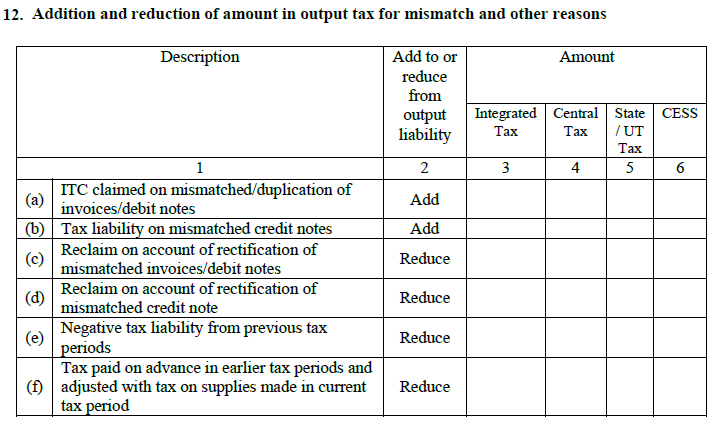
9. TDS and TCS credit received:
Receipt of TDS Credit: Applies to specific transactions e.g. supplies to government bodies, which while paying deduct the tax at source [TDS]. This is an auto-populating field.
Receipt of TCS credit:
This auto-populating section only applies to online traders with e-commerce operators, which while paying its sellers are required to collect tax at source.
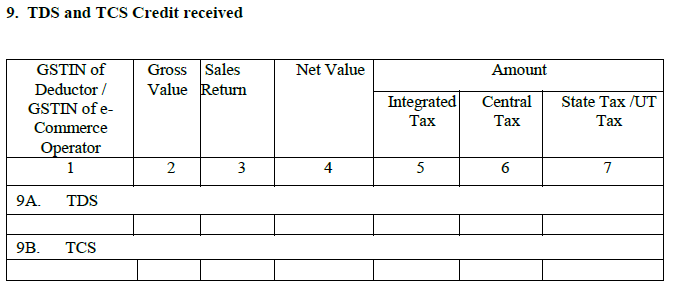
10. Consolidated statement of advances paid or adjusted with reference to receipt of supply:
This section will contain any advance payments made during the month. If the advance amount is paid on supplies which were received during an earlier tax period but the invoices have been received in the current month, furnish the details in this column.
This section also captures the details of the advance receipts issued against reverse charge.
Generally, the seller issues an advance receipt when he receives any advance payment. When the purchases attract reverse charge, the buyer should issue an advance receipt, if he pays in advance.
Part – I:
- Captures the advance amount paid for reverse charge supplies in the current month
- Includes the advance paid in earlier months against which invoices have been received in the current month.
- Purchases are segregated into inter-state and inter-state.
Part – II:
- It covers the changes to above part- I with reference to an earlier month.
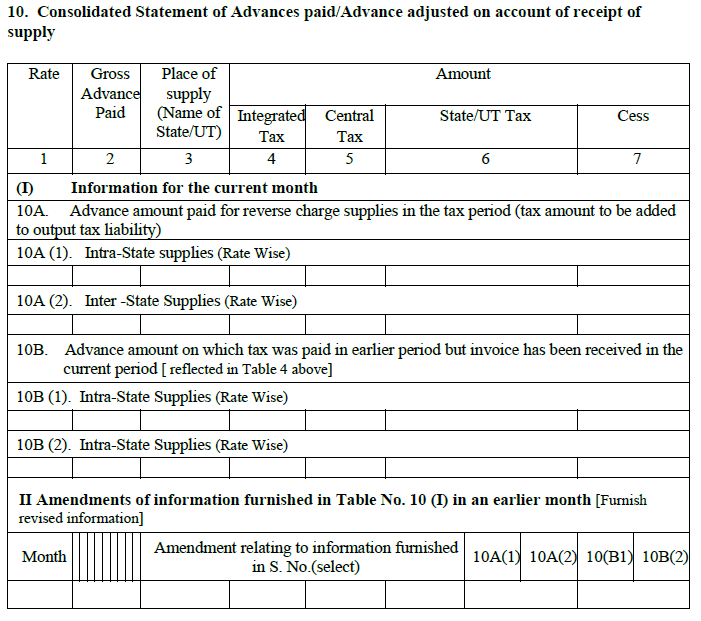
11. Reversal / reclaim of Input Tax Credit:
Transactions meant for an authorized business supply can only avail ITC. Exempt supplies do not count for claiming ITC.
This heading covers the details of ITC that cannot be claimed under different ITC rules.
11A. This column asks for all the input tax reversals for the current month including ITC reversal on account of exempt and personal supplies.
- Amount according to rule 37(2): ITC will be reversed for invoices which were unpaid within 180 days of issuance.
- Amount according to rule 39(1)(j)(ii): The section is for ISDs. When a credit note is issued by the seller to the head office, then the ITC subsequently reduced will be reversed.
- Amount according to rule 42(1)(m): Transactions which use inputs for business and personal purposes come here. ITC used in the portion of input supplies used for personal purposes should be reversed accordingly.
- Amount according to rule 43(1)(h): This is similar to above except that it concerns capital goods.
- Amount according to rule 42(2) (a): Its calculation happens after filing the annual return. If the total ITC on inputs of exempted/non-business purpose exceeds the ITC actually reversed during the year, then the difference amount will be added to output liability with applicability of interest.
- Amount according to rule 42(2)(b): In applicability, this is just the opposite of the above. If total ITC on inputs of exempted/non-business purpose is less than the ITC actually reversed during the year then the difference amount can be reclaimed as ITC.
11B. Any details of ITC under 11A of earlier months can be manually amended by selecting the correct information from the dropdown.
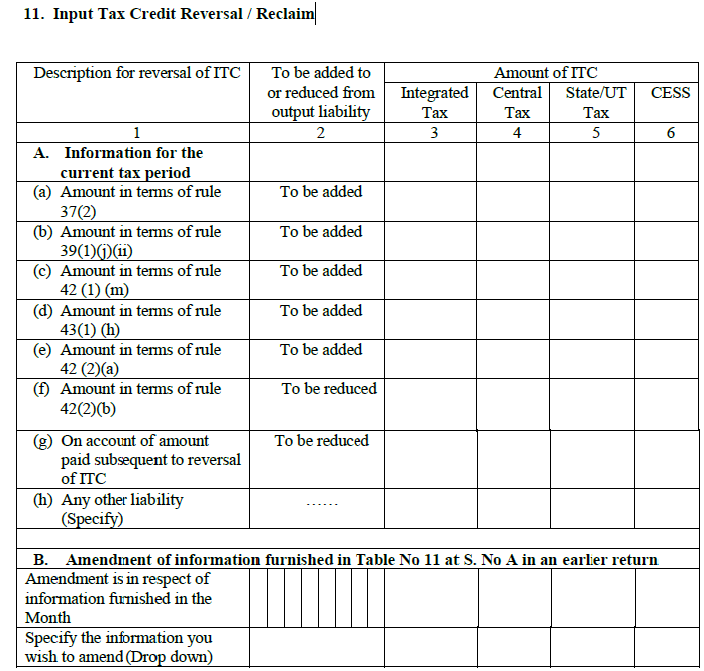
12. Amendment of amount in output tax for mismatch and other miscellaneous reasons:
Corrections made to the GSTR-3 of the previous month
- ITC claimed on mismatched/duplication of invoices/debit notes:The mismatch of invoices may lead to the double claiming of ITC. In such cases, the excess ITC claimed from duplicate purchase invoices will be reversed and added to the tax liability.
- Tax liability arising due to incorrect credit notes: Any discrepancy in the credit notes issued by the taxpayer, will also lead to a wrong ITC computation. In such cases, the excess ITC claimed from incorrect credit notes will be reversed and added to the overall tax liability.
- Reclaim for modification of mismatched invoices/debit notes: Being just the opposite of point (a), the mismatch of invoices/debit notes, in this case leads to claiming of lower ITC. The tax payer is eligible for more ITC and the additional amount will be reduced from the overall tax liability.
- Reclaim for rectification of mismatched credit note: Being just the opposite of point (b), the mismatch of credit notes in this case leads to claiming of lower ITC. The tax payer is eligible for more ITC and the additional amount will be reduced from the overall tax liability.
- Negative tax liability arising from previous tax periods: Excess tax paid in the previous months leads to having a negative tax liability, which will be reduced from the output tax liability of the current month.
- Tax paid on advance in earlier tax periods and adjusted with tax on supplies made in current tax period: The section captures the tax paid with the advance payments in earlier months for supplies received during the current month.
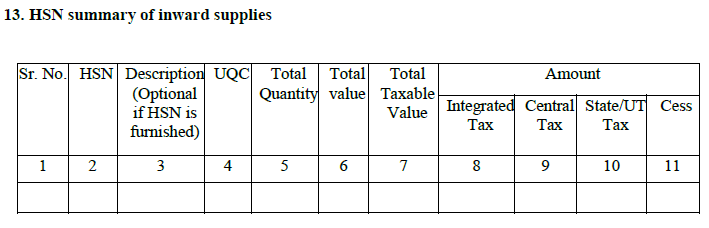
13. HSN summary of inward supplies:
The consolidated HSN wise summary of goods purchased is to be entered here by the tax payer.
Importance of GSTR-2:
The GSTR-2 captures all the purchase transactions and purchases where reverse charge applies for a calendar month and the government uses it to cross check with the sellers GSTR-1 for buyer-seller reconciliation.
Buyer-Seller Reconciliation:
The process of matching taxable sales by the seller with the taxable purchases of the buyer is known as buyer-seller reconciliation or invoice matching.
To make the ITC eligible on the purchases, the details of the purchases filed in GSTR-2 of the buyer must match with the details of the sales filed in GSTR-1 of the seller.
What if GSTR-2 is not filed / filed late?
The correct and timely submission of GSTR-2 leads to GSTR-3. In the event of not filing of the GSTR-2, GSTR-3 would also not be filed leading to heavy fines and penalties.
Should there be a delay too, it will impose interest [18% per annum] and late fees. Interest would only be charged on the outstanding amount of tax and the period considered would be from the next date of the due date [16th] to the date of payment.
Can GSTR-2 be revised?
Once filed, GSTR-2 cannot be revised and can only be amended while filing the next month’s GSTR-2. Hope, now you understand what is GSTR 2, how to file GSTR-2 or GSTR-2 return.
Should you still be confused about filing GSTR 2 and want to consult an expert, the proficient team at Masters India, a GST Suvidha Provider is here to help. autoTax from Masters India is a fully automated GST Software for return filing, which along with other functionalities also ensures that you always remain in the good books of the government by maintaining a high GST compliance rating. To know more about, on how can you put your taxation life cycle on an auto-pilot, please connect with Masters India at info@mastersindia.co | 9773706840.
- ★★
- ★★
- ★★
- ★★
- ★★
Check out other Similar Posts
😄Hello. Welcome to Masters India! I'm here to answer any questions you might have about Masters India Products & APIs.
Looking for
GST Software
E-Way Bill Software
E-Invoice Software
BOE TO Excel Conversion
Invoice OCR Software/APIs
GST API
GST Verification API
E-Way Bill API
E-Invoicing API
KSA E-Invoice APIs
Vehicle tracking
Vendor Verification API
Other Requirement


